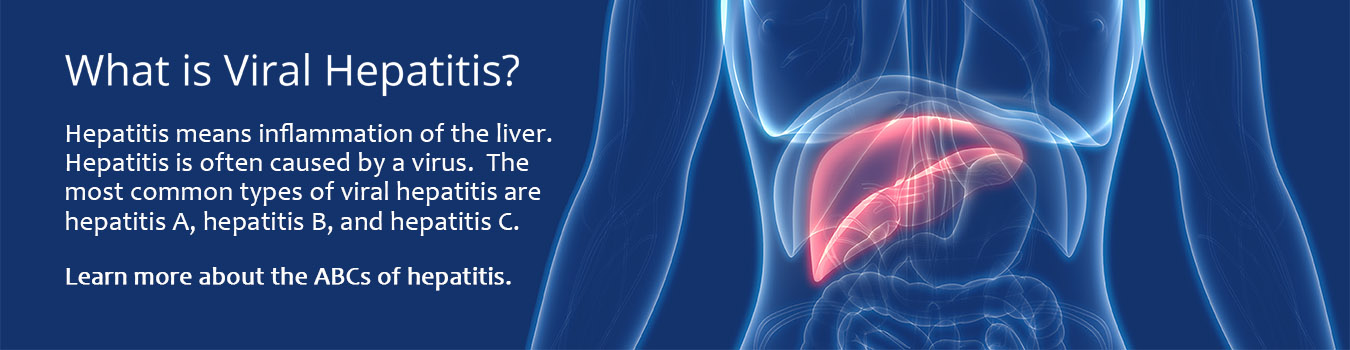
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus. It can range from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a severe illness lasting several months. Although rare, hepatitis A can cause death in some people. Hepatitis A usually spreads when a person unknowingly ingests the virus from objects, food, or drinks contaminated by small, undetected amounts of stool from an infected person.
Learn More >
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be transmitted through sexual contact, sharing needles, syringes or from mother to child. Some people may experience an acute infection that can resolve on its own while others develop a long-term chronic infection. Typically the younger the person the more likely their chances are of developing a chronic infection. 90% of infected infants become chronically infected compared to only 2%-6% of adults.
Learn More >
Hepatitis C
2.4 million people are estimated to have HCV and only half are aware of their status. Hepatitis C is an infection that can cause chronic inflammation of the liver, which can potentially lead to liver damage. This infection does result from the hepatitis C virus and can lead to an acute infection or a chronic infection.
Learn More >


